Page 16 - SW-2019-OnLine_Rev1
P. 16
WHEN THE SOLUTION BECOMES THE PROBLEM
®
BACKGROUND - Since its introduction in 1992, Energy Star certification has been the 'Holy Grail' for
manufacturers of electronics, lighting, appliances, and
building materials, especially windows. The certification
is the consumer’s assurance that the product bearing the
®
Energy Star label is among the most energy efficient
in its class. And because the designation is given only to
the top performers within their class, achieving Energy
Star certification has prompted window designers and
®
manufacturers to continually produce better and more
energy-efficient products. The Holy Grail of Performance
Four climate zones define the country
®
When first adopted, Energy Star certification was fairly easy to achieve. Usually, a thermally improved frame with an Insulating Glass Unit
would qualify. However, over the subsequent decades, the Environmental Protection Agency has required gradually improved performance
in order to qualify.
THE QUANDARY - Keeping pace with these demands for improved performance
has taken the combined efforts of the entire industry, including manufacturers and their
suppliers of framing, glass, sealants, hardware and other components. Ultimately, every
incremental performance improvement comes with an exponentially higher price tag.
Under Energy Star 6.0, the stringent U-Factor required in the Northern zone
®
(U=0.27 or better) has proven to be an extremely difficult performance level for
many manufacturers to achieve. As frequently happens, government regulations and
mandates require solutions that are beyond the performance limits of a product’s
design. When this occurs, manufacturers either replace the old product, or they Every incremental improvement costs exponentially more
explore alternate methods of meeting performance criteria, some of which may have
unintended consequences.
CHASING THE NUMBERS - In thermal testing, administered by the National Fenestration Rating Council (NFRC), windows are
measured for various performance attributes – average Air Infiltration (AI), overall Thermal Conductivity (U-Factor), potential for Solar
Heat Gain (SHGC), the percentage of Visible Light Transmittance (VT), and its overall Condensation Resistance (CRF). Each one of
these attributes are measured and reported, as they all influence energy consumption and are excellent indicators of how the window will
perform when compared to other windows.
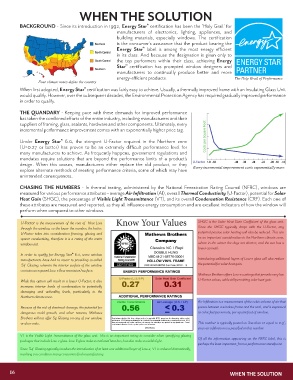
Know Your Values SHGC is the Solar Heat Gain Coefficient of the glass unit.
U-Factor is the measurement of the rate of Heat Loss
through the window, so the lower the number, the better. Since the SHGC typically drops with the U-Factor, any
U-Factor takes into consideration framing, glazing and potential passive solar heating will also be reduced. This can
spacer conductivity, therefore it is a rating of the entire be an important consideration in the Northern climate zone,
where in the winter the days are shorter, and the sun has a
window unit.
lower azimuth.
®
In order to qualify for Energy Star 6.0, some window
manufacturers have had to resort to providing so-called Introducing additional layers of Low-e glass will also reduce
'S4' Glazing, wherein the interior surface of the window the potential for solar heat gain.
contains an exposed Low-e (low emmissive) surface.
Mathews Brothers offers Low-e coatings that provide very low
While this option will result in a lower U-Factor, it also U-Factor values, while still permitting solar heat gain.
increases interior levels of condensation to potentially
damaging and unhealthy levels, particularly in the
Northern climate zone.
Air Infiltration is a measurement of the cubic volume of air that
Because of the risk of sheetrock damage, the potential for passes between a window frame and the sash, and is expressed
dangerous mold growth, and other reasons, Mathews as cubic feet per minute, per square foot of window.
Brothers will not offer S4 Glazing on any of our window
or door units. This number is typically posted as ‘less than or equal to 0.3’,
since air infiltration is a pass/fail at that number.
VT is the Visible Light Transmittance of the glass unit. This is an important rating to consider when specifying glazing
packages that include Low-e glass. Low-E glass reduces radiated heat loss, but also reduces visible light. Of all the information appearing on the NFRC label, this is
perhaps the least important, from a performance standpoint.
Since 'S4' Glazing typically involves the introduction of at least one additional layer of Low-e, VT is reduced dramatically,
resulting in a condition many consumers find unsatisfactory.
16 WHEN THE SOLUTION